Unlocking the Mysteries of High Pressure Valves in Modern Engineering
High pressure valves play a critical role in a wide array of modern engineering applications, from oil and gas extraction to power generation and chemical processing. According to a recent report by Markets and Markets, the global high pressure valves market is expected to reach USD 12.5 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2021. This growth is fueled by the increasing need for efficient fluid control in high-stakes environments, where reliability and safety are paramount. As industrial processes become more complex and regulations more stringent, mastering the intricacies of high pressure valves is essential for engineers seeking to optimize performance while minimizing risk. Understanding the various types, materials, and operational mechanisms of high pressure valves is critical for ensuring the integrity and efficiency of systems under demanding conditions. This guide aims to unlock the mysteries surrounding high pressure valves, providing essential insights for professionals navigating the ever-evolving landscape of modern engineering.
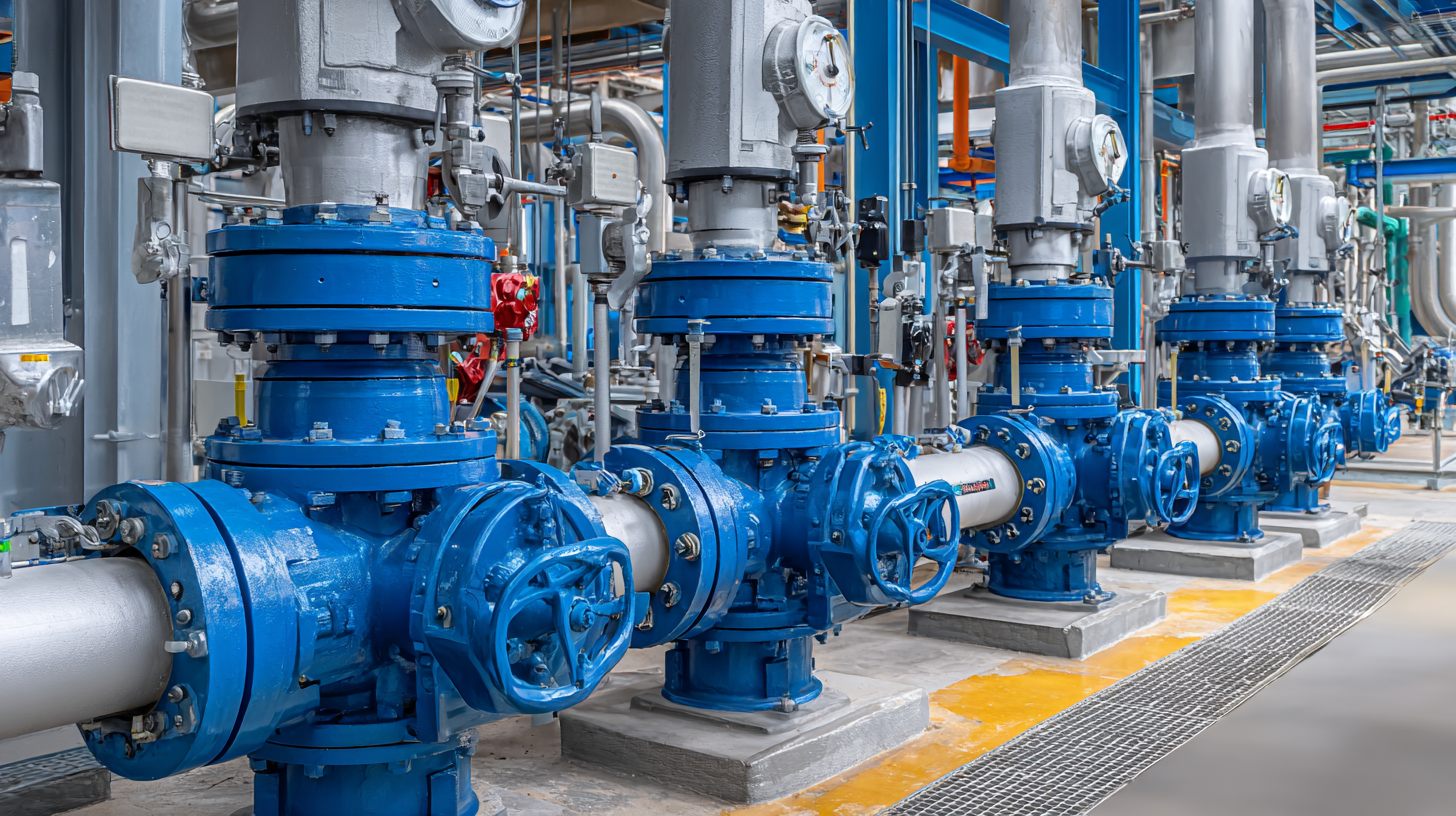

Understanding High Pressure Valves: Key Specifications and Standards in Engineering
High pressure valves play a crucial role in modern engineering applications, particularly in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. These valves are designed to control the flow of fluids under high pressure conditions, ensuring safety and efficiency. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global high pressure valve market is projected to reach $8.3 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing need for advanced energy solutions and the rise in exploration activities in untapped reservoirs.
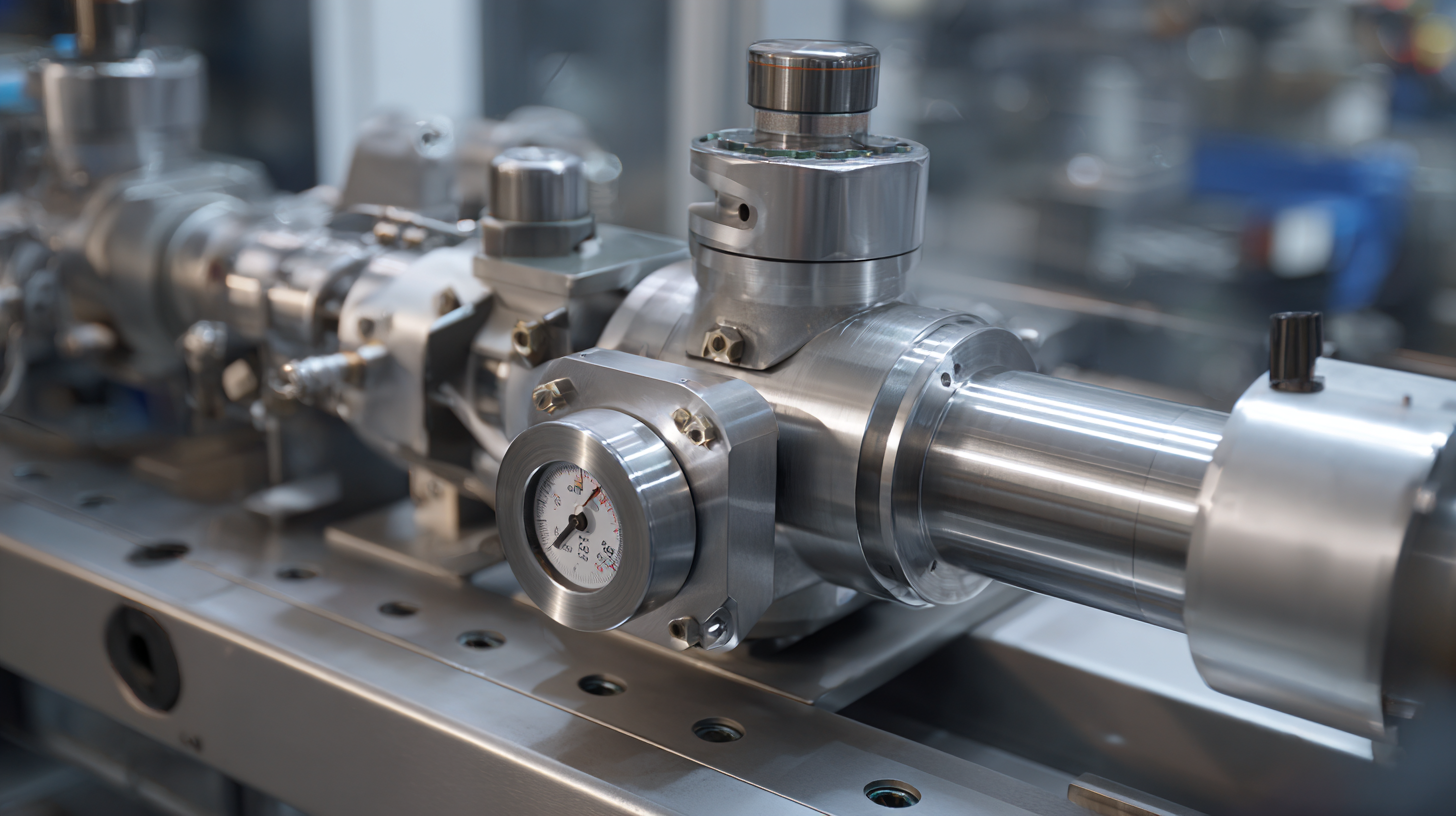
When selecting high pressure valves, it’s essential to consider specific key specifications, including pressure rating, material compatibility, and temperature resistance. Industry standards set forth by organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provide guidelines for ensuring quality and safety in valve manufacturing. For instance, valves classified under ASME B16.34 can typically handle pressures up to 6000 psi, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Tip: Always verify the valve's certification against industry standards before making a purchase. This not only ensures compliance but also mitigates risks associated with valve failure in high-pressure environments. Regular maintenance and testing are also recommended to maintain operation efficiency and longevity of the valves, as statistics indicate that up to 30% of valve failures can be attributed to inadequate maintenance practices.
Top 5 Challenges in High Pressure Valve Design and How to Overcome Them
High pressure valves play a critical role in various engineering applications, yet their design presents several unique challenges. One significant challenge is ensuring the integrity of materials used in high-pressure environments. The materials must withstand not only high pressure but also potential chemical corrosion. To overcome this, engineers should conduct thorough material selection processes and consider coating technologies that enhance durability.
Another common issue is the complexity of valve sealing mechanisms. Achieving reliable sealing is vital to prevent leaks and ensure safety. To address this, engineers can adopt advanced sealing technologies, such as using dynamic seals that accommodate movement while maintaining optimal pressure thresholds. Regular testing and simulation during the design phase can also help identify potential sealing failures early on.
Tip: Always prioritize proper training and knowledge transfer among team members to stay updated on the latest technologies and testing methods in valve design. Additionally, implementing a robust feedback loop during prototype testing can lead to continuous improvement in design processes.

The Role of Material Selection in Enhancing High Pressure Valve Performance
In the realm of modern engineering, the performance of high-pressure valves hinges significantly on the materials chosen for their construction. Selecting the right material can significantly enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and overall functionality. Engineers must consider factors such as the pressure levels involved, the type of fluids being handled, and the operating temperatures. Materials like stainless steel, titanium, and various alloys offer unique advantages that can lead to improved performance and longer lifespans of these critical components.
**Tip:** When selecting materials for high-pressure valves, always assess the environmental conditions and the specific requirements of each application to ensure compatibility and reliability.
Moreover, advancements in material science have opened new avenues in the design of high-pressure valves. For instance, composite materials and specialized coatings are becoming increasingly popular, providing lighter alternatives without sacrificing strength. Understanding the interactions between various materials can lead to innovative designs and improved safety standards in high-pressure systems.
**Tip:** Stay updated on the latest material innovations and testing standards to make informed decisions that could optimize valve performance and safety in your engineering projects.
Unlocking the Mysteries of High Pressure Valves in Modern Engineering - The Role of Material Selection in Enhancing High Pressure Valve Performance
| Material Type | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Corrosion Resistance | Temperature Range (°C) | Cost (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 520 | Excellent | -200 to 800 | $4.50 |
| Carbon Steel | 400 | Moderate | -40 to 400 | $1.50 |
| Titanium | 900 | Excellent | -250 to 600 | $30.00 |
| Alloy Steel | 700 | Good | -40 to 650 | $5.00 |
| Brass | 300 | Fair | -40 to 150 | $3.00 |
Analyzing the Impact of Pressure Ratings on Valve Lifespan and Reliability
In modern engineering, high pressure valves play a crucial role in managing fluid flow and maintaining system integrity. The pressure ratings of these valves are not merely technical specifications; they significantly impact the lifespan and reliability of the entire system. A valve designed to operate efficiently at high pressure must withstand not only the mechanical stresses but also the thermal effects of the fluid passing through it. Materials and design tolerances become essential factors that dictate how well a valve can perform over time.
Moreover, the relationship between pressure ratings and valve lifespan is complex. Higher pressure ratings typically require a thicker valve body and enhanced sealing mechanisms to prevent leaks and failures. However, this added robustness can also lead to increased wear and tear under prolonged stress, particularly in dynamic applications where pressure fluctuations are common. Engineers must carefully analyze these pressure ratings to ensure that they not only select the right valve but also implement maintenance schedules that align with the expected service life, ultimately optimizing the reliability of the system in which these valves are installed.
Innovations in High Pressure Valve Technology: Trends Shaping the Future of Engineering
The landscape of high-pressure valve technology is witnessing transformative innovations that are crucial for modern engineering applications. According to a recent market research report by Mordor Intelligence, the global high-pressure valve market is projected to reach USD 19 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2020. This growth is largely driven by advancements in materials and design that enhance the performance and reliability of valves in demanding environments such as oil and gas, aerospace, and chemical processing.
Innovations such as the integration of smart technology into high-pressure valves are reshaping the industry. IoT-enabled valves equipped with real-time monitoring systems facilitate predictive maintenance, thereby reducing downtime and lowering operational costs. Additionally, the introduction of advanced materials, such as corrosion-resistant alloys and high-performance polymers, allows for improved durability and efficiency in extreme conditions. According to the International Society of Automation, about 30% of operational costs in the oil and gas sector can be attributed to equipment failures, highlighting the potential impact of these innovations on overall productivity and safety in engineering fields.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Checklist for Selecting the Perfect High Pressure 3 Way Ball Valve
-

How to Choose the Right Pressure Valves for Your Industrial Needs
-

How to Optimize Fluid Control with a 3 Way Valve in Your System
-

Solutions for Optimal Pressure Management: Elevate Efficiency with the Best Pressure Valves
-

7 Unique Benefits of Metal Seated Ball Valves for Global Procurement Success
-

Solutions for Choosing the Best Steel Ball Valves: Key Insights from Industry Trends and Data
